Difference between revisions of "Cmc"
(→Maps built with CMC) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== CMC == | == CMC == | ||
| − | [http://www.custommapmakers.org | + | [http://www.custommapmakers.org/resources/cmc.zip CMC] is a commandline tool for semi-automatic clipping of models for Q3map2 map files. The approach carried by CMC is to automatically insert clip brushes into a map file following a "clip model" (''ie,'' a standalone map file) provided by the user. CMC consists of a python script and is licensed under beerware revision 42. Beware, the licence will be strongly enforced. |
{{Warning|Don't blame the tool if you forgot to backup your map...}} | {{Warning|Don't blame the tool if you forgot to backup your map...}} | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
=== Installation === | === Installation === | ||
| − | [http://www.custommapmakers.org | + | [http://www.custommapmakers.org/resources/cmc.zip Download CMC] from Custom Map Makers. The Zip archive contains a one file python program. Unzip and copy it to a conveniant location. |
=== Creating a ''clip model'' === | === Creating a ''clip model'' === | ||
Revision as of 11:50, 4 January 2018
Contents
CMC
CMC is a commandline tool for semi-automatic clipping of models for Q3map2 map files. The approach carried by CMC is to automatically insert clip brushes into a map file following a "clip model" (ie, a standalone map file) provided by the user. CMC consists of a python script and is licensed under beerware revision 42. Beware, the licence will be strongly enforced.
| |
Don't blame the tool if you forgot to backup your map... |
Usage
Requirements
CMC requires a working Python environment, and the argparse library (shipped with Python starting from version 2.7).
For Python versions prior to 2.7, easy_install is a convenient way to install python library (may require root privileges).
easy_install argparse
Installation
Download CMC from Custom Map Makers. The Zip archive contains a one file python program. Unzip and copy it to a conveniant location.
Creating a clip model
Create a new map, import the model to clip for reference and place its origin at the centre of the map (ie, at coordinates 0 0 0), do not rotate or scale the model. Create the clip brush around your model, once finished you can remove the model and save the clip model map.
Commandline argument
Getting help
python cmc.py --help
display a help message:
usage: cmc.py [-h] (-ls | -c model:pattern | -u clip/shader) [-o ofilename] [-d] [-v] ifile
Q3map2 map model clipper
positional arguments:
ifile q3map2 map file
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-ls, --list-shaders list all shaders
-c model:pattern, --clip model:pattern
clip models with clip pattern file
-u clip/shader, --unclip clip/shader
delete brushes using "clip/shader"
-o ofilename, --output ofilename
output file
-d, --debug
-v, --version
I map therefore I am
Clipping a model
python cmc.py --clip models/mapobjects/mymodel/mymodel.md3:maps/clip_pattern.map \
--output maps/mymap_clipped.map maps/mymap.map
maps/mymap.map
This is the path to the map to process.
--output maps/mymap_clipped.map
This instructs CMC to output the new map into the file "maps/mymap_clipped.map" (highly recommended). Without this option, CMC will overwrite the input file
--clip models/mapobjects/mymodel/mymodel.md3:maps/clip_pattern.map
This instructs CMC to clip every instance of model "models/mapobjects/mymodel/mymodel.md3" (This is not the path to the md3 file, but the model name as it appears in the entity window in GtkRadiant), according to the clip model from file maps/clip_pattern.map.
Clipping multiple models at once
python cmc.py --clip model/mymodel/mymodel.md3:maps/clip_pattern.map \
--clip model/mymodel/anothermodel.ase:maps/clip_anotherpattern.map
--output maps/mymap_clipped.map maps/mymap.map
CMC accepts any number of model/clip_pattern pair using multiple "--clip" options
Tutorial
In this tutorial, we will cover how to use CMC in order to clip a model semi-automatically. We will show how to do so in a way that facilitates modifying or removing the clip brushes even after modification of the map file.
Set up
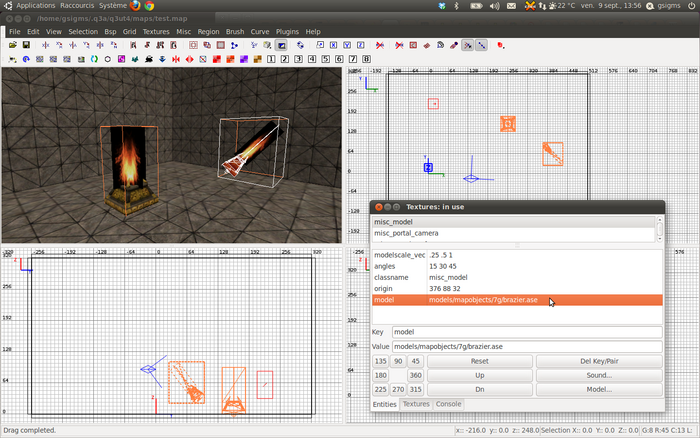
For this tutorial, you need to set up a map "test.map". This can be a simple rectangular room (Mapping:Create your first room). Add a model into your map (Radiant:Using#How_to_add_a_model), this can be any kind of model (eg, md3, ase). In this example we have a rectangular room containing two instance of a brazier model "model/test/brazier.ase". One instance is scaled/rotated in an awkward fashion, to illustrate CMC features.
Creating the clip model map
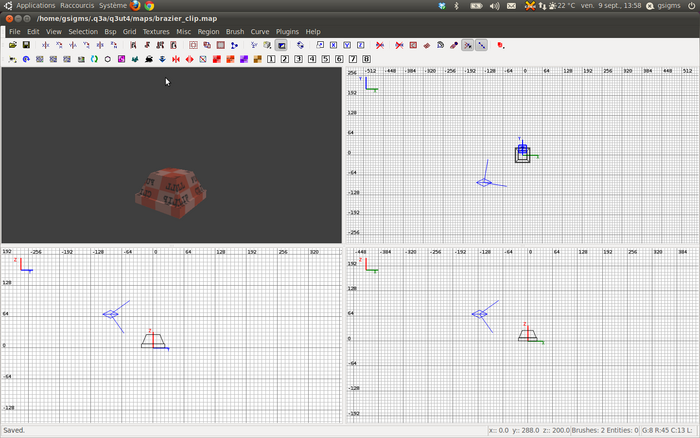
Let us now create a clip model map. A clip model map is a set of brushes that CMC is going to use as a pattern to clip our brazier model into "test.map".
Create a new map called "brazier_clip.map".
To help us draw our clip brushes, import one brazier model into the map, and place the model origin at the centre of the map (ie, coordinates (0 0 0)). It is important that the model must not be rotated or scaled here.
Now create the clip brushes around your model. It is not necessary to precisely cover every detail of the model. The purpose of a clip is to be accurate enough without being too complex. In our example, only the rough form of the base has been clipped.
Apply a "clip" shader to the newly created brushes. A clip shader is provided in the "common" shader script. But for CMC, we recommend using a dedicated shader only for CMC purpose. We will later see that this will become handy for future modifications. Here, we used a new shader called "textures/test/autoclip":
textures/test/autoclip
{
qer_trans .4
surfaceparm nodamage
surfaceparm nodraw
surfaceparm nolightmap
surfaceparm trans
surfaceparm nomarks
surfaceparm slick
}
You can optionally remove the brazier model. CMC will ignore it anyway.
Save the clip model map
Clipping the map
From this point, let us assume you extracted the CMC script into your "q3ut4" directory. Relative to the current directory, your map file path should be "maps/test.map" and your clip model map should be "maps/brazier_clip.map" run the following command:
python ./cmc.py --clip:models/mapobjects/test/brazier.md3:maps/brazier_clip.map \
--output maps/test_clipped.map maps/test.map
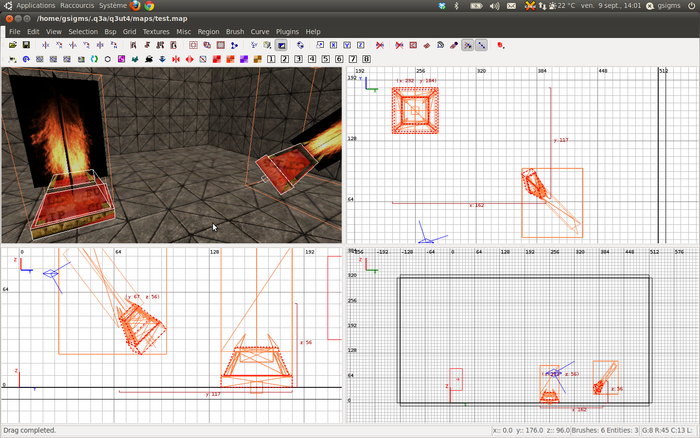
If you followed this tutorial, you should now have a new map "test_clipped.map" where CMC has automatically insert the clip brushes over your model, as shown in our example.
Because nothing is right the first time
You might realize later that your clip model brushes need some modifications. Or you may want to add new instances of your model and want CMC to clip them for you. Sadly, as of today CMC has no way of tracking models that have been clipped or replace clip brushes with a new pattern. With CMC you must first remove the clip brushes before reapplying a new clip model else you map might have duplicated clip brushes.
Hopefully, if you followed this tutorial recommendation to use a dedicated clip shader, CMC will help you do that. CMC allows you to remove every brush that has at least one face with a given shader from you map. To do that run the following command.
python ./cmc.py --unclip textures/test/autoclip \
-o maps/test_unclipped.map maps/test_clipped.map
Maps built with CMC
- Azurea: ut4_azurea_a1 is a jump map and the main motivation for building CMC. The flameholders that are also used in this tutorial have been clipped with CMC.
- Bus Stop: ut4_bus_stop_b2 is a frag map by JohnnyEnglish. Johnny used CMC to clip various models (buses, seats, garbages).
Most recently
- Nightmare xmas, a map with a lot of small models (trim, coffins, lights. presents), 12 clips used with 170 models